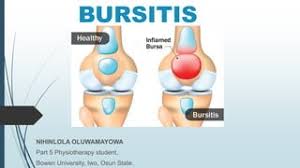
Bursitis is a condition that occurs when the bursa, a small sac filled with lubricating fluid located near joints, becomes inflamed due to repetitive motion, compression, or constant rubbing against bones and tendons. This inflammation can lead to pain, stiffness, and discomfort in various parts of the body, including the elbow, shoulder, hip, knee, ankle, and heel. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods for bursitis.
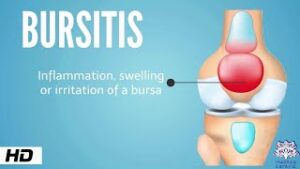
Causes of Bursitis: Bursitis is commonly caused by repetitive movements that lead to friction between the tendon and bone. Activities like throwing a ball frequently or putting pressure on joints for extended periods, such as side sleeping, can cause irritation of the bursa.
Common Areas Affected: The inflammation of the bursa can occur in different ligament regions, including the elbow, shoulder, hip, knee, ankle, and heel. The severity and location of bursitis can vary from person to person, depending on the areas that are most frequently used and irritated.
Symptoms of Bursitis: Symptoms of bursitis range from achy pain and stiffness in the affected joint area to a burning sensation that surrounds the entire joint with inflamed bursa. The discomfort is typically more pronounced during and after physical activity, and the joint area may become stiffer the following day.
Treatment Options: Proper care can help reduce bursa inflammation over a period of three weeks, but the healing process continues for at least six weeks after the initial injury. Scar tissue formation, essential for tissue bonding, can persist for several months or even up to a year in severe cases. Initially, it is crucial to support and protect the affected bursa by providing proper cushioning to prevent further friction.

- Support and Protection:
- Use supportive braces or padding to protect the affected area and reduce friction during use.
- Invest in a memory foam mattress or mattress topper to minimize pressure while sleeping.
- Topical Relief:
- Use topical solutions containing natural menthol to relieve pain and widen blood vessels without stiffening the tissue.
- Consider MSM (Methyl Sulfonyl Methane), a natural organic sulfur, known for its anti-inflammatory properties, to aid tissue healing.
- Professional Treatments:
- Ultrasound and massage therapy, performed by healthcare providers, can help break down scar tissue, restore tendon flexibility, and prevent further injury.
- Avoid Constrictive Methods:
- Ice can reduce inflammation, but it may constrict blood vessels and stiffen the joint area.
- Cortisone injections can reduce inflammation but may weaken tissue structure and promote scar tissue formation.
Prevention of Bursitis: Preventing bursitis involves regular stretching exercises to lengthen tendon connections and reduce friction. Additionally, it is crucial to minimize compression during sitting or lying down to preserve natural joint lubrication and prevent increased friction. If bursitis does occur, prompt treatment is essential to prevent its progression to a more severe stage.
By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting appropriate treatment and prevention strategies, individuals can effectively manage bursitis and maintain joint health. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific condition.